Rehabilitation continues to evolve with advancements in research, technology, and clinical practice. Physical therapists play a big role in helping patients recover from injuries, manage chronic conditions, and improve functional mobility. Incorporating innovative rehabilitation techniques into treatment plans can provide even more options for recovery and performance improvement to achieve the best outcomes for patients.
By exploring new ideas and strategies, PTs can offer personalized care that improves patient engagement, supports long-term recovery, and addresses individual movement patterns and issues. This article explores innovative rehabilitation techniques that are transforming the field of physical therapy.
Related: NDT: Current Evidence-Based Practice and Practical Advocacy for Therapy Practitioners

The role of innovation in rehabilitation
Traditional rehabilitation techniques have laid the foundation for consistently effective treatment, but integrating newer approaches can provide more benefits and help more people. Innovation in rehabilitation often involves technology, research-driven methodologies, and patient-centered techniques to optimize care.
Benefits of innovative rehabilitation techniques
There are many benefits in looking at innovative rehabilitation techniques, including:
- Improved patient engagement. Interactive and customized treatments encourage participation.
- Better functional outcomes. Addressing movement issues with new tools or strategies that increase precision leads to long-term benefits.
- Increased accessibility. Technology-based therapies offer remote treatment options.
- Personalized treatment approaches. Data-driven assessments help guide individualized care plans.
- More efficient recovery. Tailored interventions support gradual improvements without too much strain or risk of aggravation.
Upcoming innovative rehabilitation techniques
As the field of rehabilitation advances, several techniques have gained traction for their effectiveness in addressing a wide range of conditions.
Blood Flow Restriction (BFR) Therapy
BFR therapy involves applying a controlled tourniquet to reduce blood flow to a muscle group during low-load resistance training. This technique allows for strength gains without excessive strain on joints and soft tissues:
- Often used in post-surgical rehabilitation, sports recovery, and muscle atrophy prevention.
- Supports muscle growth and endurance while minimizing risk of injury.
- Effective for patients who cannot tolerate high-intensity strength training.
Virtual Reality (VR) Rehabilitation
VR-based rehabilitation programs use immersive environments to improve motor function, balance, and coordination:
- Beneficial for neurological conditions, stroke recovery, and chronic pain management.
- Increases engagement by incorporating interactive exercises.
- Allows for real-time feedback and progress tracking.
- Supports cognitive rehabilitation in individuals with brain injuries or neurodegenerative disorders.
Aquatic therapy
Water-based rehabilitation reduces the impact on joints while providing resistance for strengthening exercises.
- Helps patients with arthritis, post-operative recovery, and neurological conditions.
- Improves balance, flexibility, and endurance without excessive strain.
- Supports cardiovascular health while promoting movement confidence.
- Provides an alternative to weight-bearing exercises for those with limited mobility.
Related: Aquatic Spinal Therapy and Core Training. An Integrated Approach
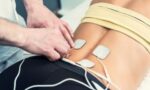
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
NMES uses electrical impulses to activate muscles, improving strength, endurance, and neuromuscular function.
- Beneficial for spinal cord injuries, stroke rehabilitation, and post-operative care.
- Aids in muscle re-education and prevention of atrophy.
- Can be used to facilitate movement patterns for patients with neurological deficits.
- Helps reduce muscle spasticity in individuals with neuromuscular disorders.
Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM)
IASTM involves using specialized tools to break down scar tissue, improve circulation, and improve mobility:
- Used for chronic pain conditions, soft tissue injuries, and post-operative recovery.
- Helps reduce muscle tension and improve fascial mobility.
- Encourages efficient healing through mechanical stimulation.
- Often combined with manual therapy techniques for a more comprehensive approach.
Related: Instrument-Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) to the Upper Quarter
Biofeedback therapy
Biofeedback therapy provides patients with real-time physiological data to help improve muscle activation and movement patterns:
- Effective for pelvic floor dysfunction, chronic pain, and postural control.
- Helps patients develop body awareness to refine movement efficiency.
- Helps reduce muscle guarding and compensatory movement patterns.
- Used in stress and anxiety management for patients with movement-related pain.
Dry needling
Dry needling is used to target myofascial trigger points and relieve muscle tension. It’s often said to have been born from acupuncture, an ancient practice based in traditional Chinese medicine. Some pros of dry needling are:
- Beneficial for chronic pain, muscle tightness, and movement restrictions.
- Helps release trigger points and improve neuromuscular function.
- Often used in combination with manual therapy for optimal results.
- Supports pain modulation in musculoskeletal disorders.
Integrating innovative rehabilitation techniques
While new rehabilitation techniques offer promising benefits, they should be implemented strategically based on patient needs, goals, and clinical indications. Some key considerations when integrating innovative techniques into a patient’s rehabilitation plan include:
Individualized treatment plans
- Assess patient history, functional deficits, and movement patterns.
- Select innovative techniques that align with patient-specific goals.
- Monitor response to treatment and adjust interventions as needed.
- Incorporate progress tracking tools to assess ongoing improvements.
Evidence-based practice
- Stay informed about research supporting emerging techniques.
- Integrate innovative approaches with standard rehabilitation principles.
- Collaborate with multidisciplinary teams to optimize patient care.
- Adapt treatments based on new clinical guidelines and patient outcomes.
Patient education and engagement
- Explain the purpose and benefits of new rehabilitation techniques.
- Encourage active participation and self-management strategies.
- Utilize digital tools and resources to improve learning and accessibility.
- Provide home exercise programs that incorporate elements of innovative rehabilitation.
Challenges and considerations for innovative rehabilitation
Despite their benefits, innovative rehabilitation techniques come with challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation:
Accessibility and cost
- Some advanced technologies require a lot of investment in equipment.
- Insurance coverage may vary, requiring alternative payment options.
- Exploring community-based resources can provide affordable alternatives.
Patient readiness and adaptability
- Some patients may be hesitant to try new techniques.
- Gradual integration and clear education can improve comfort levels.
- Providing patient testimonials and case studies can build confidence in new methods.
Clinical training and expertise
- Physical therapists have to stay updated on best practices for implementing new rehabilitation techniques.
- Continuing education courses help develop proficiency and confidence in new or specialized techniques.
- Facilities should invest in staff training programs to make sure that new techniques are properly done.
Conclusion
Innovative rehabilitation techniques offer new ways to improve patient outcomes, increase engagement, and support long-term recovery. Physical therapists can expand treatment options and address diverse patient needs by integrating evidence-based approaches like blood flow restriction, VR rehabilitation, and neuromuscular electrical stimulation.
Staying informed, adapting to new technologies, and personalizing treatment plans will continue to shape the future of physical therapy and rehabilitation. As the field progresses, adopting a patient-centered approach and remaining adaptable will help physical therapists provide effective and forward-thinking care.